Summary
Image-based 3D modeling uses photogrammetry, AI-powered 3D reconstruction to create 3D models from images, offering an accessible, cost-effective alternative to conventional 3D capture solutions. This technology is used across industries as diverse as aerospace, gaming, architecture, and e-commerce, supported by a range of open-source and professional software. While facing some challenges, advancements in AI, cloud computing, and AR/VR integration are shaping the future of 3D reconstruction.
Highlights
| Methods for 3D model creation from images | Applications | Software |
|---|---|---|
| Photogrammetry and AI-powered 3D reconstruction. | Aerospace, gaming, real estate, and retail | Meshroom, COLMAP, Agisoft Metashape, RealityCapture, Artec Studio19. |
Introduction
In today’s digital culture, creating 3D models from images has become an essential technique, transforming industries such as gaming, film, design, architecture, e-commerce, and even healthcare.
This process, also known as photogrammetry, transforms 2D photographs into ultra-accurate, detailed 3D models. With the growing demand for lifelike digital assets, virtual environments, and authentic reconstructions, individual professionals and businesses are embracing image-based 3D modeling as a cost-effective and efficient solution. Visual effects, product visualization, heritage preservation, or engineering – whatever it is used for, this technology is reshaping the way we capture and interact with the world around us.
What is 3D reconstruction from images?
3D reconstruction from images is the process of creating 3D models from a set of 2D photographs. This technique helps us generate highly detailed and realistic digital twins of objects, environments, or landscapes using standard camera images.
One of the most commonly used methods is photogrammetry, which works on multiple overlapping images to determine depth, shape, and texture by identifying common reference points.
Another innovative approach is AI-powered reconstruction, where machine learning algorithms make 3D model generation more accurate and efficient by predicting missing details and improving surface textures.
These techniques are widely used in a diverse range of industries, from gaming and VR to archaeology and construction to retail, offering both powerful and accessible ways to digitize real-world objects into interactive 3D assets.
KEY POINT: 3D reconstruction from images means generating 3D models from a series of 2D photographs. Two common techniques include photogrammetry and AI-based reconstruction.
Advantages of creating 3D models from images
Cost-effectiveness
While precise and reliable, conventional 3D scanning methods may require costly specialized hardware, making them less accessible for smaller businesses and makers. In contrast, image-based 3D modeling using photogrammetry or AI-based reconstruction slashes costs by relying on standard cameras while still producing high-quality results, with no need for pricey scanning equipment.
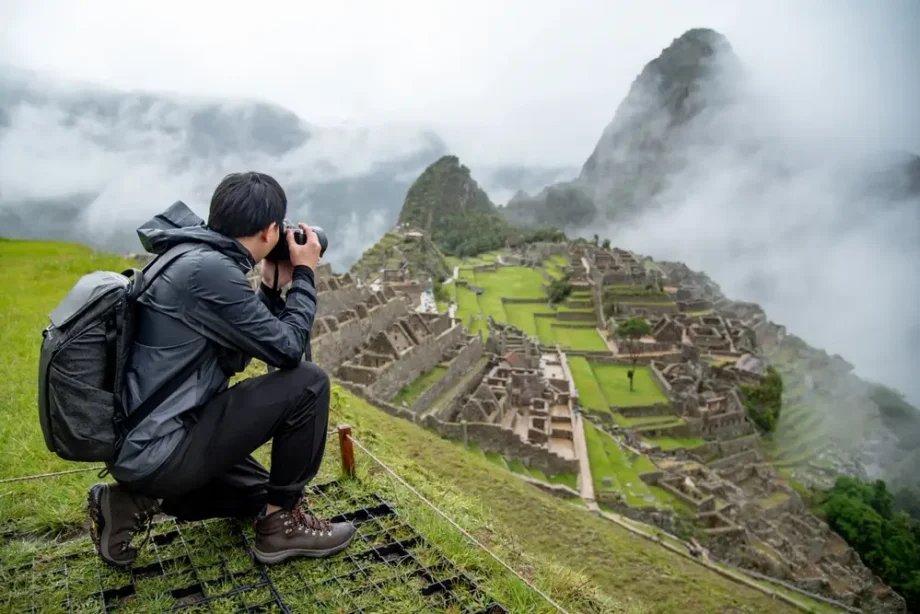
One great example is digitally reconstructing the ruins of Pompeii back in 2023. By capturing thousands of images with drones and DSLR cameras, researchers created watertight 3D models of fragile structures, preserving every detail at a fraction of the cost of traditional 3D scanning methods.
Accessibility
One of the biggest pros of this approach is that it is genuinely easy to use – all you need is a camera or a smartphone. This makes 3D model creation widely available to virtually anyone, allowing both seasoned professionals and hobbyists to generate realistic 3D assets without sophisticated tech knowledge or specialized equipment.
A great choice of user-friendly software also lowers the entry barrier. Retail corporations like IKEA or Zara have integrated smartphone-based 3D modeling into their websites, allowing companies to create 3D models of their products with just a smartphone camera. Such accessibility has potential for small retailers who are looking to develop next-gen AR experiences for customers and improve online shopping customer experience.
Scalability
Image-based 3D modeling is a versatile and scalable solution, adaptable for industries as diverse as gaming, VR, design, architecture, heritage preservation, and online retail. Whether reconstructing small items for product visualization or capturing massive-scale environments for urban planning, the flexibility of this technology makes it a valuable tool across multiple fields.
KEY POINT: Image-based 3D modeling is a cost-effective, accessible, and scalable alternative to conventional 3D capture solutions.
Methods for 3D model creation from Images
There are several techniques to make 3D models from images, each with its own advantages and applications. Let’s explore three of the most commonly used methods: photogrammetry, AI-powered reconstruction, and depth estimation techniques.
Photogrammetry
A widely used method, photogrammetry reconstructs 3D models by analyzing multiple photos of an object or scene shot from different angles. It works by identifying common points in overlapping images and using this data to calculate depth and geometry. The more images and angles are captured, the more realistic and accurate the resulting 3D model will be.

Structure from Motion (SfM) is the main technique within photogrammetry. SfM algorithms detect matching features across multiple images, determining their relative positions and reconstructing a 3D point cloud of the object. This data is then processed to generate a detailed textured 3D model.
Some versatile photogrammetry tools include:
A professional-grade photogrammetry software, Agisoft Metashhape is commonly used in archaeology, GIS, and game development for creating precise 3D models.
With innovative tools for dense point cloud generation, texture mapping, and georeferencing, the software is great for research and commercial uses.
Its workflow supports drone imagery and large datasets, which is crucial for detailed reconstructions in archaeological and geographical applications in particular.
A tool acclaimed for its processing speeds and top-quality reconstructions is a go-to choice for large-scale projects in urban modeling, architecture, or art conservation.
The software can handle great amounts of image and LiDAR data, which allows users to produce accurate 3D models with minimal manual input.
The software integrates with a diverse range of platforms and game engines, which also makes it popular among VFX and game design professionals.
This open-source photogrammetry software is free, flexible, and designed with accessibility in mind.
Meshroom relies on AliceVision’s advanced reconstruction pipeline to generate 3D models from images.
Featuring a node-based interface, allowing users to customize and refine the reconstruction process, it is a go-to choice for makers, educators, or researchers looking to explore photogrammetry.
AI-powered 3D reconstruction
AI-based 3D reconstruction utilizes machine learning and deep neural networks to generate lifelike 3D models, often with fewer input images than traditional photogrammetry. AI algorithms are trained on massive datasets of real-world objects, so they can enhance textures and depth perception, and fill in missing details.
AI-based approaches often use Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs), encoding light and geometry data to create renderings of complex surfaces. Instead of simply storing geometric meshes or textures, NeRFs learn a volumetric representation by mapping spatial coordinates and viewing angles to color and density values, providing novel view synthesis with photorealistic detail. This approach streamlines capturing complex lighting effects, such as reflections, translucency, and sophisticated textures, making it handy for applications in computer graphics and VR.
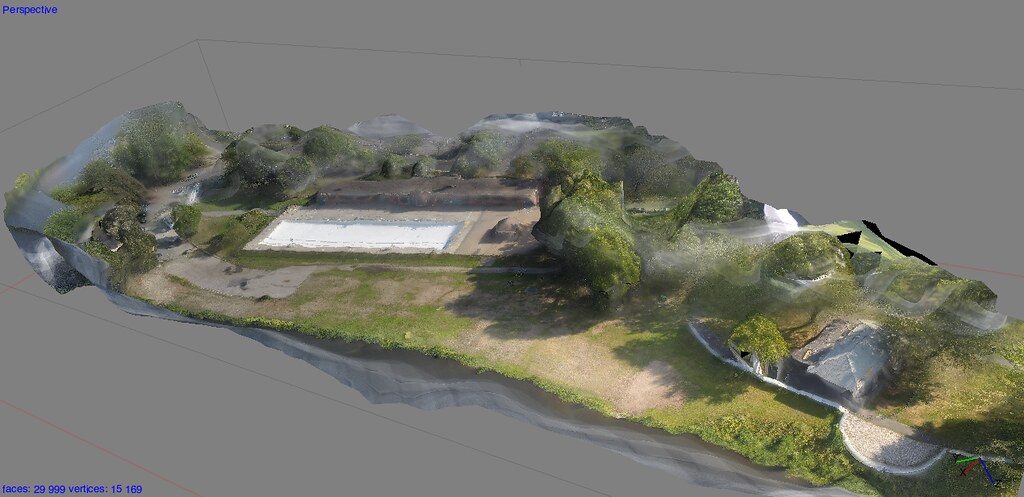

Some examples of AI-based 3D reconstruction technologies are NVIDIA Instant NeRF and Google’s DeepSDF. The former uses Neural Radiance Fields to generate 3D scenes from just a few input images, while the latter is a deep learning method for shape representation, where AI can generate digital twins based on prior knowledge.
Depth estimation and stereo imaging
This method uses specialized cameras, such as dual-lens (stereo) cameras or LiDAR sensors, to capture depth information directly while taking images. Instead of reconstructing depth mathematically from multiple images (like photogrammetry), these devices measure depth in real-time.
In stereo imaging, dual-lens cameras take two images simultaneously from slightly different angles, mimicking human binocular vision to estimate depth. RGB-D cameras like Microsoft Kinect capture both color (RGB) and depth (D) data for instant 3D mapping. LiDAR sensors, in turn, are used in self-driving cars and smartphones, such as the iPhone Pro series. LiDAR uses laser pulses for precise distance measurements, creating high-accuracy depth maps.
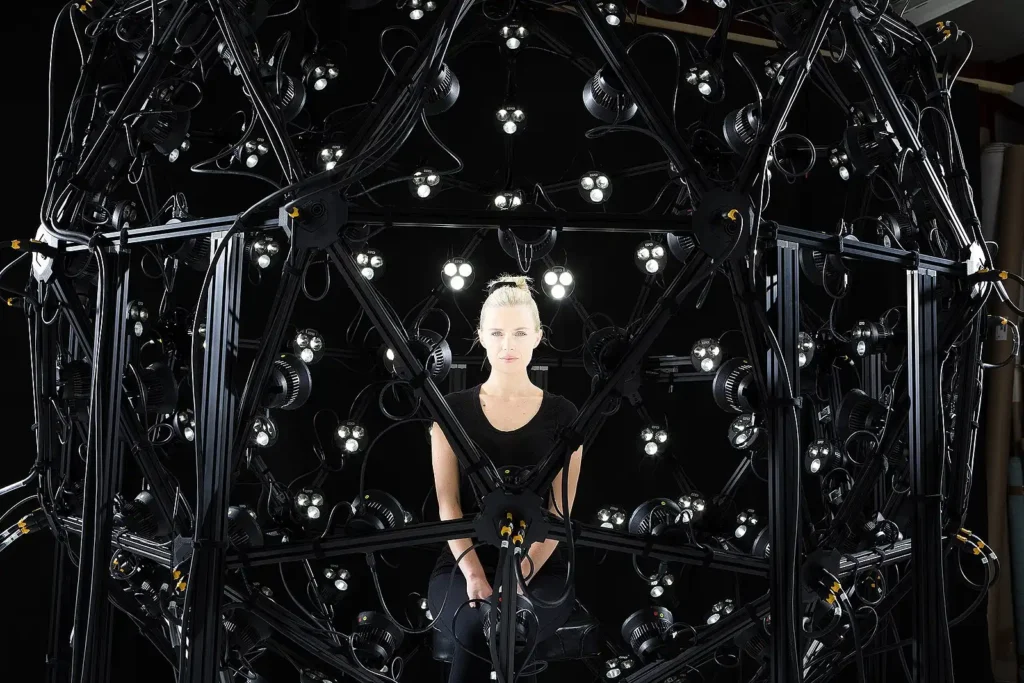

Two interesting examples of devices for depth estimation are Intel RealSense, a compact depth-sensing camera used for robotics, AR, and industrial applications, and Apple LiDAR scanner, integrated into iPhones and iPads for improved AR experiences and quick 3D scans.
KEY POINT: The three main methods for creating 3D models from images include photogrammetry, AI-powered reconstruction, and depth estimation, each using a different technology, from feature matching and neural networks to specialized sensors.
Software and tools for 3D model generation
Making 3D models from images requires specialized software to process multiple photos into detailed digital twins. These tools come in a variety of functionality, price, and computational requirements, catering to both beginners and professionals. Here are some of the most widely used solutions, categorized into open-source and professional-grade software.
Free/open-source software
Meshroom

Developer: AliceVision
Platform: Windows, Linux
Technology: Structure from Motion (SfM) & Multi-View Stereo (MVS)
As mentioned above, Meshroom is an advanced computer vision framework, allowing users to generate 3D models from multiple images by automatically detecting key points and matching them across photos to reconstruct a dense point cloud and a textured 3D mesh.
Key features:
- Fully open-source and free, hence great for makers, students, and researchers.
- Node-based workflow for customizing the reconstruction pipeline and modifying depth estimation, feature extraction, and meshing.
- CUDA acceleration for faster processing times.
- Seamless integration with Blender, Maya, or Unity for further refinement.
Best for:
- Beginners looking to explore photogrammetry.
- Researchers in need of customizable workflows.
- Creative professionals seeking a free alternative to pricey solutions.
COLMAP

Developer: ETH Zurich
Platform: Windows, Linux, macOS
Technology: Structure from Motion (SfM) & Dense Reconstruction
COLMAP is another open-source photogrammetry tool, especially popular in academia and research. Unlike Meshroom, COLMAP is more focused on accurate 3D reconstruction in scientific applications that often require command-line interaction for advanced configurations.
Key features:
- Highly accurate SfM pipeline, producing top-quality camera pose estimations and reconstructions.
- CUDA-compatible NVIDIA GPUs for rapid processing.
- Depth map and stereo fusion for highly detailed 3D models.
- Command-line and GUI options, operation through a graphical interface or terminal for advanced scripting.
Best for:
- Users who need highly customizable pipelines.
- Researchers studying computer vision and/or photogrammetry.
- Professionals looking for a powerful alternative to advanced commercial software.
Professional software
Agisoft Metashape

Developer: Agisoft
Platform: Windows, macOS, Linux
Technology: Photogrammetry (SfM, MVS), AI-Assisted texture generation
Price: from $179 (standard) to $3,499 (professional)
Agisoft Metashape is a professional photogrammetry software intended for high-precision 3D reconstruction. Preferred by architects, archaeologists, surveyors, and VFX artists. Agisoft Metashape boasts high accuracy and automation features.
Key features:
- Automated, fully streamlined workflow, from image alignment to mesh generation.
- High-resolution DEM and orthophotos for geospatial applications like GIS mapping and drone surveys.
- AI-powered denoising and texture mapping.
- 3D reconstruction with infrared, LiDAR, and multi-spectral cameras.
Best for:
- GIS professionals and surveyors who need ultra-accurate 3D terrain models.
- Film and game design applications requiring high-resolution 3D assets.
RealityCapture

Developer: Capturing Reality (acquired by Epic Games)
Platform: Windows
Technology: Photogrammetry and AI-based reconstruction
Price: Subscription-based, depending on usage.
RealityCapture is a fast photogrammetry solution, widely adopted by game developers, architects, and VFX studios. Its GPU-accelerated algorithms guarantee rapid processing compared to conventional photogrammetry tools.
Key features:
– Full GPU parallelization for ultra-fast reconstruction.
– Gigapixel images processed with no quality loss.
– Seamless integration with Unreal Engine.
– Efficient scaling for city-wide mapping and infrastructure projects.
Best for:
– Game developers using lifelike 3D environments.
– Urban planners and architects working on large-scale reconstructions.
– Filmmakers integrating 3D scans into CGI-heavy productions.
Artec Studio 19

Developer: Artec 3D
Platform: Windows
Technology: AI-Photogrammetry and 3D Scanning
Price: from $800 per year (based on license type).
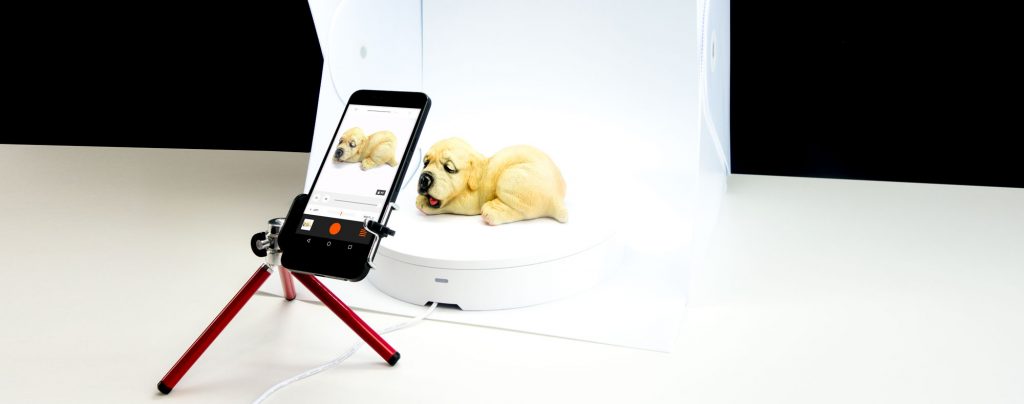
AI photogrammetry feature in Artec Studio integrates data from virtually any camera-equipped device, including smartphones – which makes it entirely possible for anyone to process images or videos from their phone to create a watertight 3D model. In addition to image-based processing, Artec Studio leverages AI algorithms to minimize noise, enhance data alignment, and boost texture mapping, resulting in ultra-realistic digital twins. Capture and upload images or videos from your device, and let the advanced algorithms do the rest of the job, that is automatically align images and detect fine features to reconstruct a detailed 3D model, ready for refinement or immediate use.
Key features:
- Compatible with any photo or video data and incredibly diverse datasets.
- Hybrid workflow, supporting LiDAR, laser, and structured light 3D scanners.
- AI-powered object reconstruction recreating fine details, translucent and featureless surfaces.
Best for:
- Anyone looking to create a true-to-life 3D model from images or videos.
- Manufacturers, medical professionals, and heritage preservation specialists requiring precise 3D models.
KEY POINT: Software for image-based 3D model generation ranges from open-source tools like Meshroom and COLMAP, which offer customizable workflows for educators and hobbyists, to advanced professional solutions like Artec Studio 19, Agisoft Metashape, or RealityCapture, which provide high-precision, AI-driven reconstructions for geospatial industries, architecture, VFX, and heritage preservation.
Key Applications of 3D Models from Images
The ability to produce 3D models from images has transformed numerous industries, boosting workflows, enhancing visualization, and minimizing costs and effort. Let’s dive into some of the most impactful applications of image-based 3D modeling across various sectors.
Aerospace and engineering
Whether for NASA, airspace firms, or major airlines, 3D models generated from images are instrumental in analysis, testing, and predictive maintenance.
Simulation and testing: Engineers use photo-based 3D reconstructions to model aircraft components, engines, and entire aerospace structures for virtual stress testing and performance analysis without physical prototypes.
Predictive maintenance: Airlines and manufacturers leverage AI-driven photogrammetry to capture aircraft parts for detecting potential wear and tear before any issues arise.
Reverse engineering: Photogrammetric 3D scanning allows professionals to recreate legacy parts for maintenance and reproduction, even with no access to original blueprints.
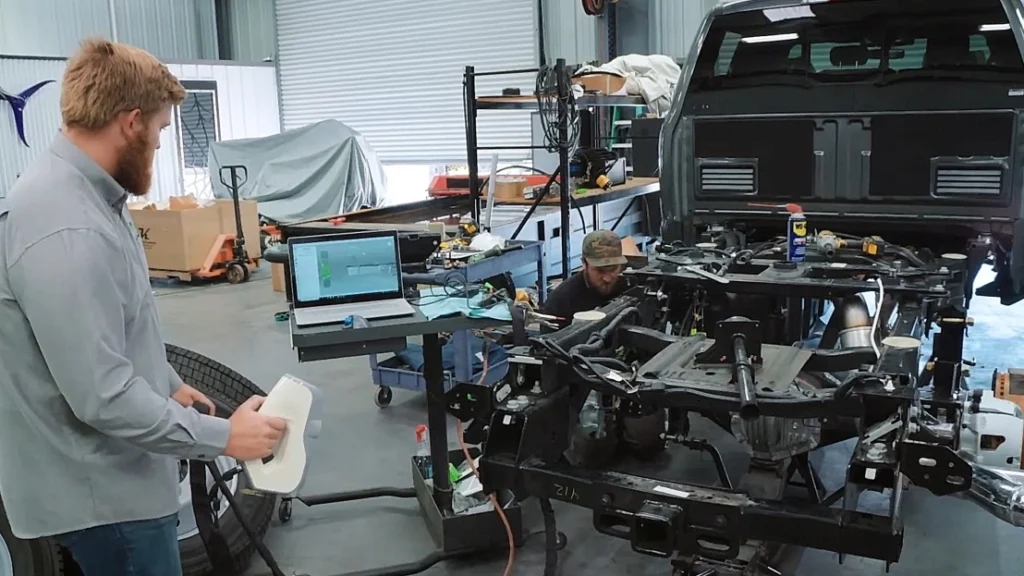
Gaming and AR/VR
The gaming industry and AR/VR applications rely on image-based 3D modeling and AI-generated models to create immersive digital environments. This technique is key to realistic asset generation in shorter time and at a lower cost compared to manual 3D modeling.
Photorealistic game environments: Developers can scan real-world locations to generate authentic landscapes and structures for open-world games.
AR applications: Whether for retail or social media apps, photo-based 3D models enable virtual try-ons and interactive ads.
VR training and simulations: Medical, military, and aviation industries use 3D reconstructions for VR training programs, freeing teams from dependence on physical setups.

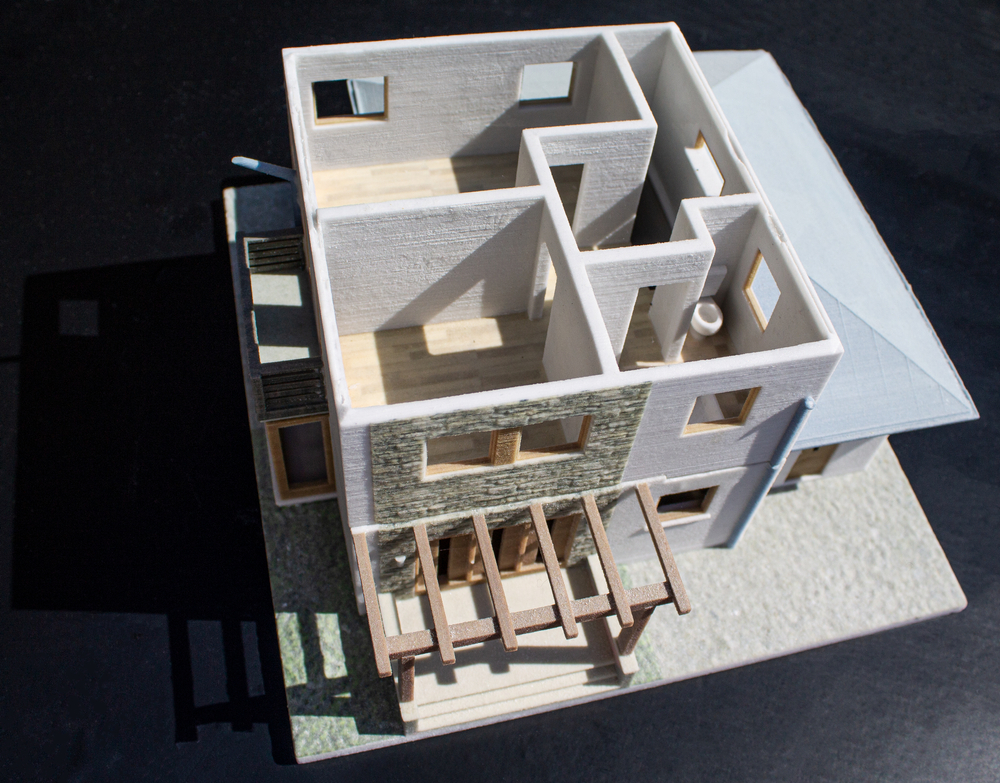
Architecture and real estate
Architects, urban planners, and real estate professionals use 3D models from images to visualize and market properties with unbeatable accuracy.
Virtual walkthroughs and pre-construction visualization: both architects and clients can examine detailed 3D representations of any building before construction begins, minimizing errors and improving design.
Smart cities and BIM (Building Information Modeling): Urban infrastructure planners can optimize urban development, traffic flow, and zoning plans with the help of photogrammetry-based 3D models.
Real estate marketing: Digital twins of properties allow buyers to do virtual tours of homes remotely, providing an interactive experience for increased buyer confidence.
E-Commerce and retail
In the booming sector of online shopping, 3D models from images have taken product visualization and customer engagement to a completely new level.
Virtual try-ons: Online retailers use AI-driven 3D modeling for product reviews, letting customers try on clothing, accessories, or even furniture and interior elements through AR applications.
Next-gen shopping experience: 3D product models provide 360-degree views, boosting customer confidence and bringing return rates to minimum.
Automated assets generation: Using image-based 3D modeling, businesses can rapidly convert 2D product photos into interactive digital replicas, eliminating the need for manual techniques requiring more investment.
KEY POINT: Creating 3D models from images has been crucial in a diverse range of applications by enabling aerospace and engineering to enhance simulation and maintenance, gaming and AR/VR to generate immersive 3D environments, architecture and real estate to improve visualization and planning, and e-commerce and retail to revolutionize product interaction and marketing.
Key challenges and limitations of image-based 3D model creation
Despite its growing adoption by professionals across the world, image-based 3D modeling comes with technical challenges that can affect the accuracy and efficiency of the reconstruction process. These limitations may require specialized techniques and hardware to overcome.
What are three major challenges we could face when generating 3D models from images?
Lighting and shadows
One of the common issues in photogrammetry and AI-based 3D reconstruction is inconsistent lighting. These methods rely on capturing multiple photographs from various angles, so any shadow, reflection, or variations in lighting conditions may lead to incorrect depth estimation and distortions in the final result.
Uneven light intensity creates inconsistent textures, so it becomes difficult for algorithms to align images accurately. Shadows, appearing in one image but not in others, provoke false depth data in the reconstruction process. Poor lighting conditions generally reduce feature detection accuracy, meaning models are low-quality or incomplete.
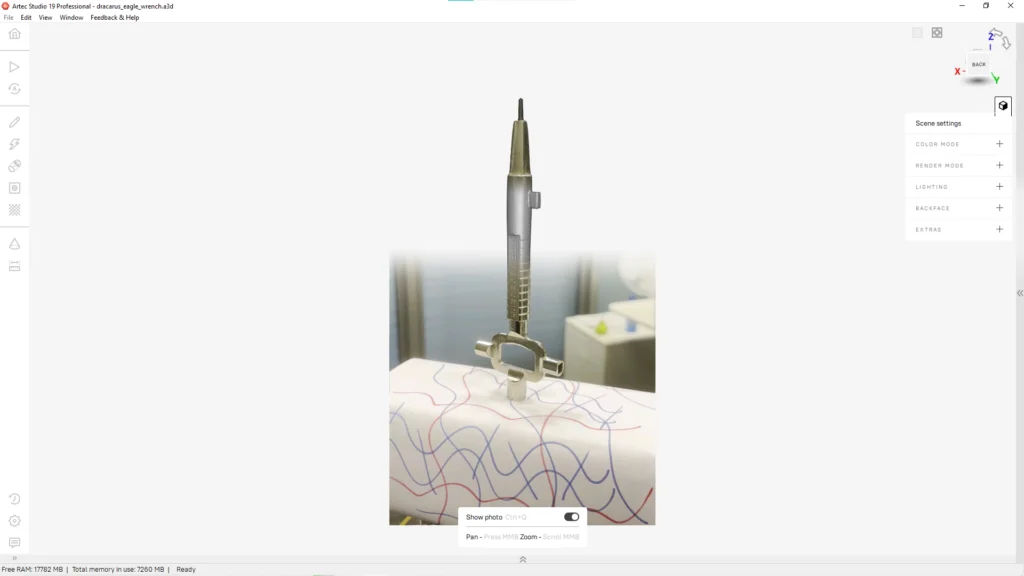
A potential solution to this challenge is trying to set up even and diffused lighting when capturing images to avoid strong shadows and overexposure. For outdoor capture, opt for cloudy weather or shoot during golden hour when shadows become softer. AI-based denoising and shadow-removal algorithms can also enhance image consistency before processing.
Reflections and transparency
Glass, mirrors, and reflective surfaces are all significant challenges for image-based 3D reconstruction because for the majority of algorithms it is still a struggle to interpret translucent or highly reflective materials. This can result in missing geometry, distorted depth maps, or even duplicate objects in the final model.
The problem is that glass and transparent materials normally do not create reliable feature points, so the software cannot detect depth and surface details. Mirrors and reflective surfaces trick reconstruction algorithms by duplicating objects, while high-gloss materials like polished metals, may introduce specular highlights, interfering with point matching.
What we can do here is apply spray coatings or polarizing filters to reduce reflections and improve image consistency. It is a good idea to capture multiple angles against clear backgrounds to improve the visibility of transparent objects. Some software, however, like AS 19’s AI-Photogrammetry is capable of overcoming this challenge and digitizing even tricky-to-capture translucent surfaces.
Computational power
Generating high-res 3D models from images requires robust computing power, especially when dealing with massive datasets or ultra-detailed reconstructions. This can become a limiting factor for users with no access to high-end hardware or cloud computing resources.
Processing hundreds or thousands of images demands powerful GPUs and high RAM capacity, while high-resolution textures and dense point clouds require extensive storage and memory. All this increases processing time and file sizes. 3D reconstruction in real time is also computationally expensive, so it is challenging to do in mobile or browser-based environments.
Nevertheless, we can utilize cloud-based 3D processing platforms to offload computation to remote servers and AI-accelerated algorithms to slash processing time. Optimizing models can be done by reducing polygon counts and applying efficient texture mapping with visual quality uncompromised.
KEY POINT: Major challenges for image-based 3D modeling are lighting and shadows affecting depth accuracy, reflections and transparency resulting in missing or distorted geometry, and computational power limitations demanding high-end hardware or cloud-based solutions for efficient processing.
Future trends in image-based 3D model creation
The future of creating 3D models from images is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in AI, cloud computing, and extended reality technologies. These innovations are set to make 3D model creation much faster, more accessible, and incredibly immersive across a range of industries.

AI-driven automation for faster and more accurate 3D reconstruction
AI is revolutionizing photogrammetry and depth estimation, making 3D reconstruction blazing fast, more automated, and more accurate, competing with or adding to other advancements like text-based AI 3D modelling.
- AI-powered techniques like NVIDIA Instant NeRF allow for rapid 3D reconstruction from just a few images, eliminating the need for large datasets.
- With AI-based texture mapping, machine learning models are able to automatically enhance textures, remove artifacts, and fill in missing details, minimizing manual corrections.
- Deep learning for object recognition can segment images into separate objects, backgrounds, and materials, making it easier to generate structured 3D models.
Cloud-based 3D modeling for accessibility and efficiency
Cloud computing has shifted 3D modeling workflows and made them more scalable and accessible – with no need for high-end local hardware.
- Cloud processing with services like Google Cloud Vision or NVIDIA Omniverse allow users to work with complex 3D reconstructions on remote servers.
- Collaborative 3D workflows have become possible with cloud-based platforms, as teams across different locations can now work on the same 3D models in real time.
- On-demand 3D rendering means users can generate 3D content with high fidelity from mobile devices without requiring powerful GPUs.
Integration with AR/VR for immersive experiences
As augmented and virtual reality become more and more mainstream, 3D models from images are being increasingly used to create interactive, one-of-a-kind immersive experiences.
- Real-time 3D environments for VR are entirely possible with photorealistic digital twins integrated into virtual worlds for gaming, training simulations, and virtual tourism.
- AR-based product visualization allows retailers and manufacturers to enable product previews in their real-world environment.
- AI-powered motion capture for lifelike digital avatars is more and more common in metaverse applications.
KEY POINT: The future of image-based 3D modeling is defined by AI-driven automation for faster and more accurate reconstructions, cloud-based processing for accessibility and collaboration, and AR/VR integration for immersive experiences across industries.






